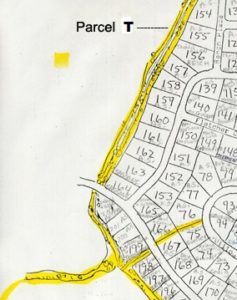
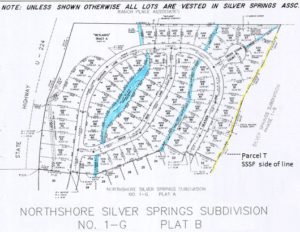
Parcel T – Drainage Channel
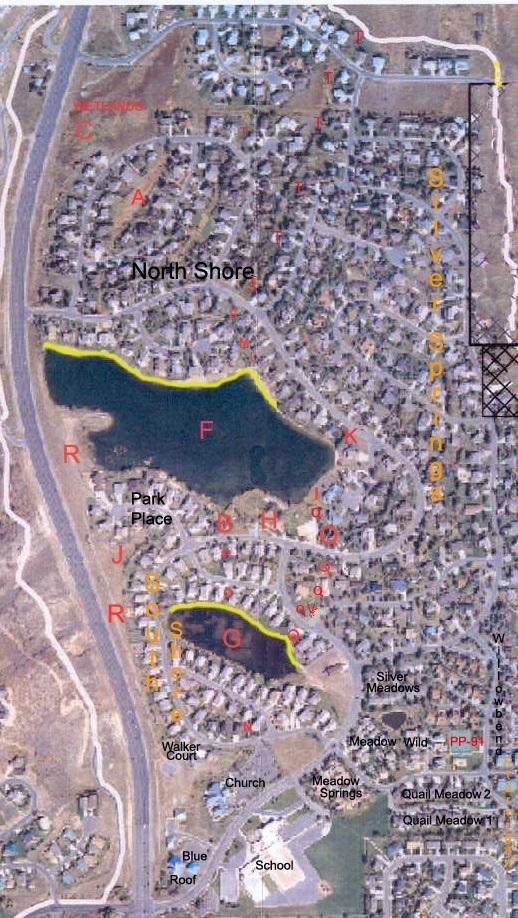
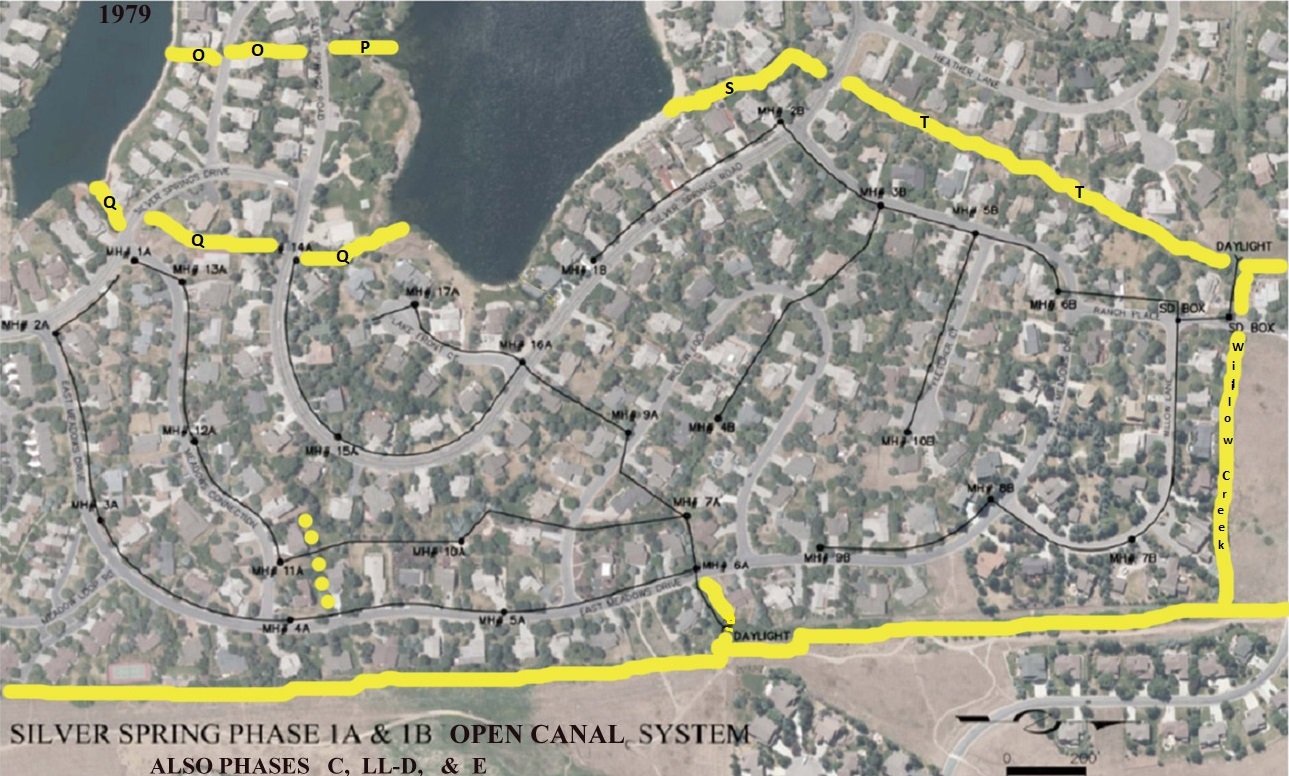
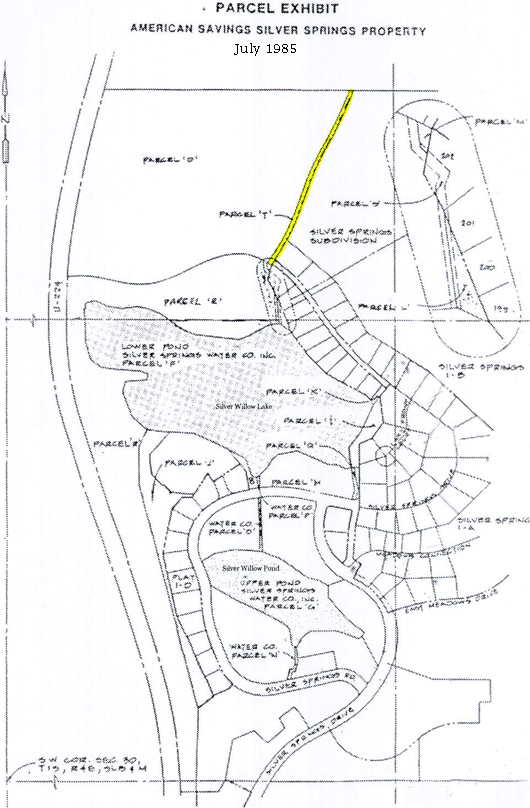
Parcel T : Common area, begins as approximately 15′ wide drainage easement commencing at Silver Springs Road between North Shore Lot 22 and Silver Springs Lot 164, then runs north to Ranch Place. Am. Sav. Parcels A, S, and T as shown on the map exhibits below. One or more of these water easements are described in the 2002 Quit Claim Deed to the Master Association, Entry 616573. The remaining parcel(s) belong to NorthShore HOA.
Parcel T – common area stream outlet on right side of plat, runs through Ranch Place toward Swaner Nature Preserve.
The stream outlet area south of Silver Springs Road is Parcel S.

Fall of 2009- north off Heather Lane

2008 – Parcel T drainage creek – between NS Lot 45 and 46

Bridge over Parcel T drainage creek between NS Lots 45 and 46
Parcel A is on the left. Parcel T on the right. T may belong to NorthShore subdivision.
Presently, July 2008, this waterway is choked with cattails and other weeds.

North border of NS Lot 46 and Ranch Place

2008 – Parcel T creek is choked by Indian Grass.
View from Ranch Place toward Heather Lane
Cattail Control
Cattails are colonial plants rising from creeping stems called rhizomes like a branching shrub on its side. The creeping rootstock of underground rhizomes is one means of reproduction to rapidly spread cattails locally while the seeds are another way cattails establish new colonies. The common cattail can grow up to nine feet in height.
Cattails can quickly ruin a pond’s visual and recreational benefits. Control is best achieved through disruption of the root system. Cutting cattails 2 or 3 inches under the waterline 2 or 3 times to drown them can actually stimulate them if done in May. Pulling them out by the roots can be impractical and costly to dispose.
Cattails are perennial wetland plants found growing above the surface of the water in marshes, ditches, shoreline shallow areas of lakes, ponds, slow streams, quiet water up to 4 feet deep, and seasonal flood areas.
Although widespread throughout most of North America, Europe, Asia, and Africa, cattails are not llikely to grow in depths exceeding 18″ to 24″ or areas not wet most of the growing season.
Cattail seeds germinate in April and plants mature from July through August.
We recommend Avocet with Cide Kick II for easy control without digging up the landscape or concern over maintaining water level.Using our treatment method, herbicide travels throughout the plant killing both the roots and vegetative portions. Simply spray on the portions of the cattail that can be reached. There is no need to spray from multiple directions.
Restore the visual and recreational value of your property through optimum treatment results.
Contact Lake Restoration at 1-877-428-8898 for application tips regarding timing, affects of weather, results, and more.

Intersection of NorthShore Lot 46, SSSF Lot 154 and Ranch Place Parcel C